Nadene Goldfoot
Paleo Hebrew lettersThe Hebrew language is around 3,000 years old.
The world in 1,000 BCE or 3,024 years agoThe oldest evidence of written Hebrew dates back to the 10th century BCE, A 10th century BCE example of a year would be 950 BCE; as the 10th century BCE spans from 1000 BCE to 901 BCE.
The Hebrew Bible was written in Hebrew. Our history is that Moses wrote the first 5 books called the Torah. Moses lived according to Jewish history from 1391 BCE to1271 BCE; a total of 120 years. What he wrote may have been in Egyptian hieroglyphs. "Often referred to as Torah, especially when in scroll format, the Five Books of Moses are the foundation of Judaism. Until this very day, the text—which is written in Hebrew (for us today)—has been carefully preserved by the Jewish people."
The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE.
Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity.
For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as Lashon Hakodesh (לְשׁוֹן הַקֹּדֶש, lit. 'the holy tongue' or 'the tongue [of] holiness') since ancient times.
The language was not referred to by the name Hebrew in the Bible, but as Yehudit (transl. 'Judean') or Səpaṯ Kəna'an (transl. "the language of Canaan").
Mishnah Gittin 9:8 refers to the language as Ivrit, meaning Hebrew; however, Mishnah Megillah refers to the language as Ashurit, meaning Assyrian, which is derived from the name of the alphabet used, in contrast to Ivrit, meaning the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet.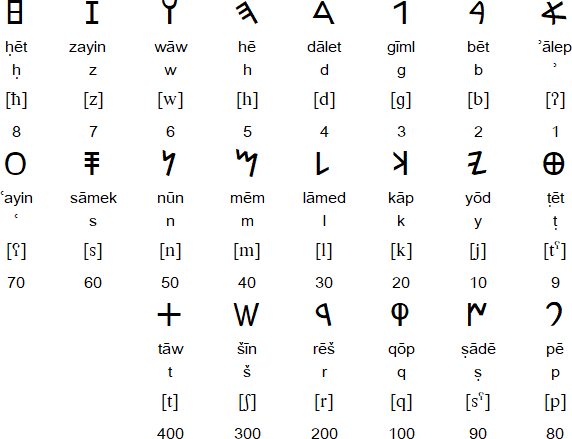
The Paleo-Hebrew alphabet was used between about 1,000 BC and 135 AD to write Ancient Hebrew in the Biblical regions of Israel and Judah.
It developed from the Proto-Canaanite script, which was used in Canaan (the Levant) during the Late Bronze Age. Paleo-Hebrew is also known as the Proto-Hebrew or Old Hebrew script.
The earliest known inscription in Paleo-Hebrew was found on a wall in Tel Zayit in the Beth Guvrin Valley in southern Israel in 2005. It dates from about the 10th century BC. By the 6th century BC the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet was gradually replaced by the Imperial Aramaic alphabet, which developed into the Hebrew square script. The Paleo-Hebrew alphabet continued to be used for some texts of the Torah, and also on coins, until the 2nd century CE.
Notable features of Hebrew is that :
- Type of writing system: abjad / consonant alphabet
- Writing direction: right to left in horizontal lines
- Used to write: Ancient Hebrew
- There are no separate numerals, instead each letter has a numerical value.
- Example is the number 18: made up of khet(8) and yud(10)=18. or Chai
-
usually pronounced like the English word “hi” or “high,” which is a word and symbol that means “life.” In fact, a common Jewish toast “L’Chaim!,” which means, “To Life!” is often said at celebrations in anticipation of all the good things to come.
Judaism is a religion that emphasizes the importance of life and the hope that supports it. As a result, 18 is a popular number that represents good luck. At weddings, bar mitzvahs, and when making honorary donations, Jews often give gifts of money in multiples of 18, symbolically giving the recipient the gift of “life” or luck.
Hebrew itself as a spoken language was: Hebrew inscriptions from the 10th century BCE show that the language was similar to Phoenician and other Canaanite languages. Hebrew fell out of spoken use for centuries and was mainly used for writing and scholarly study. "The Hebrew language is attested in inscriptions from about the 10th century BCE, when it was almost identical to Phoenician and other Canaanite languages, and spoken Hebrew persisted through and beyond the Second Temple period, which ended in the siege of Jerusalem (70 CE). It eventually developed into Mishnaic Hebrew, which was spoken until the fifth century.
Resource:




No comments:
Post a Comment